Forex exchange has given rise to one of the world’s largest marketplaces, where millions worldwide are traded currencies. With more than $5 trillion transacted daily, the forex market is the most liquid in the world.
Unlike other marketplaces, there is no centralized location where traders meet to exchange currencies in the forex market. Instead, the forex market is simply a network of banks, brokers, retail, and institutional investors that connects to do business.
Being a global market with limited entry barriers, the forex market is opened five days a week, 24 hours a day. Forex brokers are at the heart of providing platforms that allow traders or financial institutions with currency needs to transact for whatever reason. It is in these platforms that traders worldwide post buy and sell orders of currencies on the network.
What Kind of Market Access Do Forex Brokers Offer
Forex brokers at the heart of facilitating trading in the forex market offer direct market access. In this case, the brokers provide a platform that allows clients to interact and transact directly with large banks, market makers, and other traders.

The emergence and proliferation of internet-based trading systems have made direct market access more accessible than ever. In such settings, traders are accorded direct access to the market without any intermediaries. In this case trades are placed with liquidity providers such as foreign exchange banks and market makers.
Direct market access, as offered by forex brokers, occurs with the help of sophisticated technology infrastructure. In this case, DMA brokers deal with large financial institutions with operations on the interbank market. The banks are tasked with providing liquidity in real-time while dealing in huge volumes of foreign currencies.
In return, the forex brokers who offer trading platforms aggregate bid-ask prices from the liquidity providers and transmit the same to clients. In the end, retail traders and institutional traders can see actual market prices from where buy and sell orders are triggered.
In this case, traders can see several quotes from which they can choose the bid-ask price. The broker could then send an order directly to the interbank market for execution. All transactions triggered are executed in real-time along with the bid and ask price. Besides, traders can see market depth, i.e., buying or selling, at what particular price, and the level of the trading volume.
How Forex Interbank Market Works
The interbank market is the epitome of the forex market, whereby traders from large financial institutions trade against each other. The market segment also attracts reputable hedge funds and trading firms with sizable financial muscle than the ordinary investor.
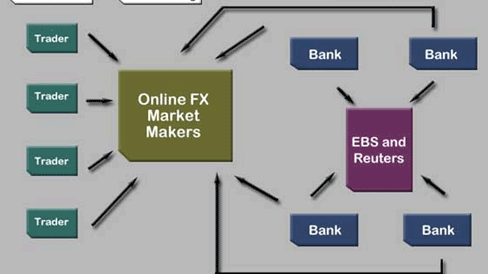
The FX interbank market flow accounts for almost 50% of the value of transactions transacted in the overall forex market daily. While large financial institutions can trade directly, they can also transact through electronic FX interbank platforms.
The interbank market serves the primary role of providing the much-needed liquidity in the decentralized forex market. A financial institution must be deemed creditworthy to be allowed to trade in the interbank market. The same is done by signing the ISDA agreement.
Centralized Forex Explained
What is a centralized exchange?
A centralized exchange is simply a trading platform that functions like a traditional brokerage or stock market. The exchange is owned and operated by a company that maintains total control of all transactions in the market.
In a centralized exchange, traders or users don’t directly access private keys or exchange account wallets. All the user’s trust is put in the hands of exchange operators. Also, transactions can only be made through mechanisms and operations approved by the exchange’s central authority.
An excellent example of a centralized market is the New York Stock Exchange or the Chicago Board of Trade, whereby each transaction is recorded by price and volume. All transactions that take place can be traced back to the centralized exchange.
The stock market is fully centralized. What this means is that there is usually an exchange that facilitates the buying and selling of stocks. The New York Stock Exchange is one such centralized exchange that enables people to buy and sell stocks.
Decentralized Forex Market
A decentralized marketplace is one where there is no central exchange. The absence of a central intermediary means there is a direct interaction between buyers and sellers.
The forex market is decentralized as there is no one single exchange where all trades are recorded. Trading activities around currency pairs take place all over the world on multiple exchanges. There is no single characterization of an exchange listing, as is the case with the New York Stock Exchange or the CBOE.
In the forex market, there is also no single clearinghouse for Forex transactions. In this case, every single market maker or financial institution records its trades.
Centralized vs. decentralized forex trading: Pros and Cons

Fees
Centralized and decentralized trading differ a great deal when it comes to trading fees. Forex trading has become increasingly popular because of the low trading fees that traders are subjected to, given the market’s decentralized nature. In the forex market, transactions that would ultimately cost $1000 can cost as little as pennies.
In contrast, centralized trading can be expensive as centralized exchanges charge a percentage of every transaction. While the exchanges provide a more robust trading tool, the trading charges can be extremely high.
Anonymity
Decentralized forex trading also stands out in part because of the anonymity that the exchanges offer traders. With centralized exchanges, market makers must collect a robust amount of personal information to stay in compliance with the Anti-Money Laundering Laws.
In contrast, decentralized exchanges don’t have any central authority, thus not required to collect any personal information. Likewise, a trader can sign up and start trading in the forex market without any identification or verification.
Liquidity
Centralized marketplaces stand out given the high liquidity that they offer most of the time. Likewise, centralized exchanges have a significant lead over decentralized forex trading, given the high liquidity levels always on offer. High liquidity enables fast transaction execution speeds as well as stable prices.
A bad actor in a decentralized forex market can put in fraudulent orders that go undetected all to manipulate price direction. It is usually a big problem whenever forex brokers do not establish trust.
Bottom Line
The forex market is the largest marketplace globally, with a daily turnover of more than $4 trillion. The marketplace is decentralized as there is no single exchange whereby all trades are recorded or central authority to control everything.
The decentralized nature of the forex market has given rise to low trading fees compared to centralized exchanges. Similarly, decentralization ensures the protection of people or firms with dealings in the market.