Forex involves the act of trading – buying and selling – currencies, hoping that the rate of exchange moves in favor of the investor. One of the fundamental principles that one should be aware of in Forex is that of the bid-ask spread. A trader should be able to tell a currency pair’s spread and calculate it. In this guide, we go through how one can do so and some essential factors that influence it.
What is forex spread?

The prices at which the buyers and sellers are willing to trade are called the bid and ask prices respectively. In Forex, the bid price is the level at which the broker buys a base currency in exchange for the quoted currency. Whereas, the ask price is the level at which s/he sells the base currency for the quoted currency.
The Forex spread is the difference between the lowest and the highest price at which a currency can be bought and sold. Therefore, if you start a sell trade, you will get quoted the bid price; if you start a buy trade, the ask price will be given.
How to calculate the forex spread
All forex currencies are quoted with the bid and ask prices. Here is an example of how a forex broker might quote a currency pair, such as the EUR/USD with the spread into it.
EUR/USD
| BID | ASK |
| $1.1200 | $1.1240 |
| Sell | Buy |
In the example above, let’s say you want to go long and buy Euros with the bid price quoted as $1.1200 on the broker’s platform. If you want to buy, you would be given the ask price of $1.1240 as given above. If the Euros bought were returned immediately to the broker, you would receive the bid price of $1.1200 (assuming no change in the exchange rate). Put another way, the extra cost of $0.0040 was the cost that you accrue due to the spread.
Depending on the currency pair, the spread can be either narrow or wide. The spread of 40 pips in our example is considered wide and unusual. In actuality, it may only be a few pips (one to five). But, these do fluctuate and can change at the drop of a hat if market conditions are suited for it. One can even find the percentage through the following:
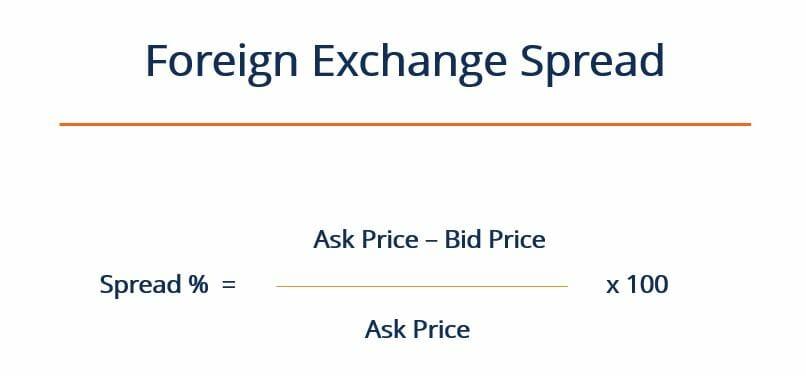
Traders have to track and monitor the spread given by the broker as their trades have to profit them enough to cover up the spread as well as any fees involved. This is because brokers do add their fees to the spread that increase their profits for every trade initiated. If there is a wide spread, it would mean that you, the trader, would have to pay more for buying and get less for selling. Every broker will charge differently and add to the spread of the forex trade.
Factors that influence the forex bid-ask spread
Other than the brokers’ fee, certain other factors determine the widening or narrowing of a forex spread. These are as follows:
1. Time of day
The spread may change depending on the time of the initiation of the trade. If the trade is conducted at times when it is unusual for that currency to be traded, there won’t be much liquidity as there won’t be many traders. Due to a lack of liquidity, the currency won’t easily be traded as the market is lacking in participants. As such, the spreads will be widened by the brokers to safeguard themselves from the risk of a loss.
For instance, European trading opens in the early hours for American traders and Asia trading opens late relative to the two. If you trade the Euro during the Asian session, you will get a wider trade than if you had traded during the Euro session.
2. Trading volume
A simple heuristic that applies to almost all financial markets is that if the market has a high trading volume, the spread is going to be low. The logic is simple; if there are more buyers and sellers, the probability that you’re going to find those willing to conduct trades is higher. In a market where there are greater buying-selling volumes, the spread will be narrower since the bids rise and asks fall.
3. Economic and political risks
Spreads widen during times of economic and political uncertainty. For instance, if there is uncertainty over elections and the future of economic policies in the UK, the spread between USD and GBP would go up.
Traders are averse to risks and slow down their trading activity until the times are better again. Spread will widen on the back of fewer active traders. However, uncertainty also comes with its own opportunities as those who can predict or forecast future events successfully can make a significant profit.
4. Currency volatility and liquidity
During certain events, forex markets can move quite suddenly and be extremely volatile. This can pose a challenge for a broker to determine the exact exchange rate. As such, in order to account for the risk of loss, the spread is wider. Furthermore, certain pairs are more liquid than others that determine the volatility and, in turn, their spread.
5. Presence of dealers and banks
Other than traders, there are some institutions and banks that don the role of a dealer in the forex market. Their source of profit is the buy-ask spread and they do not hold fast to any currency for a long time. The higher the number of such dealers in the market, the lower the spread will be.
Conclusion
The bid-ask spread in forex should be seen as the dealers’ and the brokers’ profit margin. The more of them there are in the market, the lower the spread will be since the competition amongst them for the traders’ funds squeezes out the margins.
However, their presence (and absence) is ascertained by numerous factors, some of which we have discussed above, which ultimately drive the spread of a particular currency pair.