The bond market is often unknown to many novice investors. In fact, Robinhood, a platform popular among retail investors, does not offer these assets. Yet, they are the biggest asset class in the world. For example, according to Tradeweb, the daily average volume of bonds in its platform is more than $1.08 trillion. In this article, we will look at how you can use treasury yields in the financial market.
How the bond market works
To understand treasury yields, we need to look at how the bond market operates. For starters, a bond is a type of loan that companies and governments borrow from the financial market. These loans offer a cheap way to access capital without ceding control to the lenders.
2020 was the busiest year in the bond market in recent years as companies and countries rushed to borrow to fund the coronavirus response. The United States Treasury Department borrowed more than $4 trillion in the market. Most companies also relied on cheap bonds to survive.
The bond market works in a relatively simple way. First, a company or country comes up with an amount of money they want to raise. Second, they talk to banks and other financial intermediaries to structure these bonds.
Third, rating agencies like S&P Global, Fitch, and Moody’s assess the borrowers and come up with a rating. Think of it as a credit score that helps lenders know whether the borrower is creditworthy. Finally, they go to the market, issue the bonds and raise the money. They will then pay back interest as agreed.
The duration of bonds can range from a few months to decades. In recent years, some countries like Austria and Mexico have issued 100-year bonds.
How bonds are priced
Bond pricing is a relatively complicated thing because of the number of details that are involved. Still, the overall pricing of bonds depends on several factors. The most important is the duration. Ideally, longer-dated bonds usually attract a higher return than shorter-dated ones. This is simply because of the fact that it is easier to predict what will happen in one year than in 30 years. Therefore, longer holders usually demand a higher return.
The price of a bond is also affected by the overall interest rates. If a central bank cuts interest rates, the obvious outcome is that the bond prices will increase. Similarly, if rates rise, the bond prices usually decline.
Importantly, bond yields move in the opposite direction as prices. When bond prices fall, the overall yield will increase, and vice versa.
Treasury yields in forex
Forex and other traders pay close attention to activities in the bond market for two reasons. First, bond yields are good predictors of inflation or the overall economic activity. In turn, these activities usually have an impact on how a central bank makes interest rates. Indeed, Central Bank officials pay close attention to the bond market than stocks.
Second, in the past, the Treasury yield curve has been an accurate predictor of recessions. Therefore, this information can guide you on what currency to buy or sell.
Treasury yield curve and recessions
A closely-watched item in the bond market is the yield curve. This is simply the arrangement of yields of short to long-term bonds. As mentioned, in normal periods, short-term bonds have a lower yield than longer-dated bonds. This is known as a normal yield curve.
However, at times, investors will demand a higher yield for shorter bonds than the longer ones. This happens when investors start anticipating significant short-term challenges for the economy. It is known as a yield curve inversion and is one of the most accurate predictors of a recession in the market.
Indeed, as shown below, the curve inverted in 1999, 2007, and 2019. In 2000, there was the dot com bubble, while in 2008, there was the Global Financial Crisis. In 2020, the American economy went through the coronavirus pandemic. The chart below shows that recessions came shortly after the inversion.
Yield curve inversion
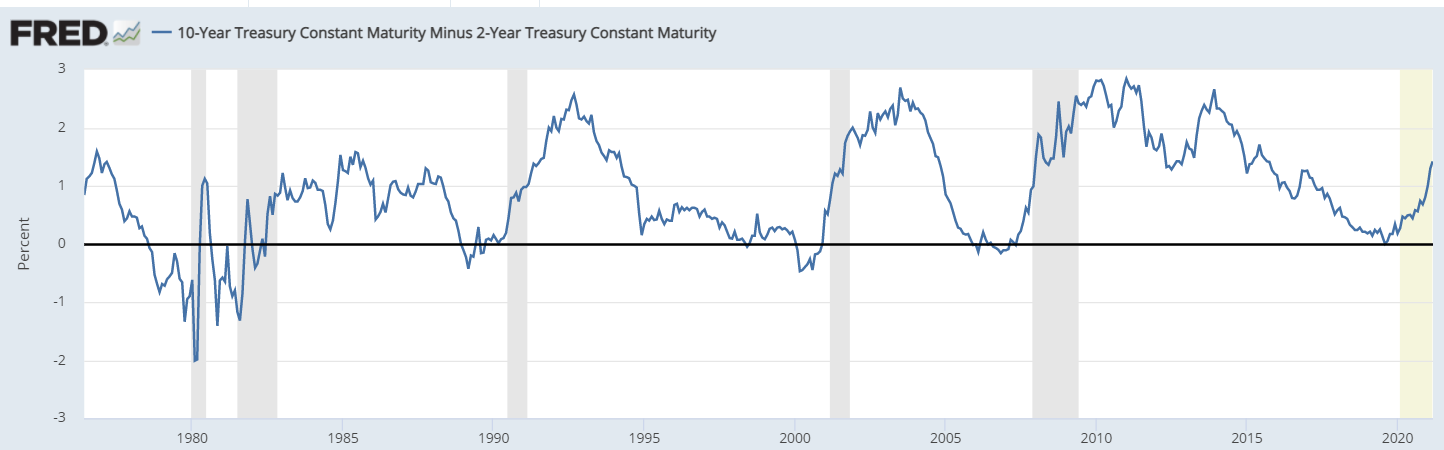
Finally, there is a flat yield curve, which is when the yield of short and long-term bonds is the same. A flat curve is not popular, and it usually happens when the normal yield curve is transitioning to a flattened curve.
Implications of the yield curve in forex
The implication of a yield curve in the forex market is that when yields are rising, there is a general feeling that the central bank will hike interest rates. This is because rising yields are an indicator that investors are pricing-in inflation to happen in the future. When inflation rises, a central bank usually hikes interest rates to normalize the situation. When rates rise, in theory, a country’s currency tends to rise. The chart below shows the five-year breakeven rate, which is a good inflation predictor.
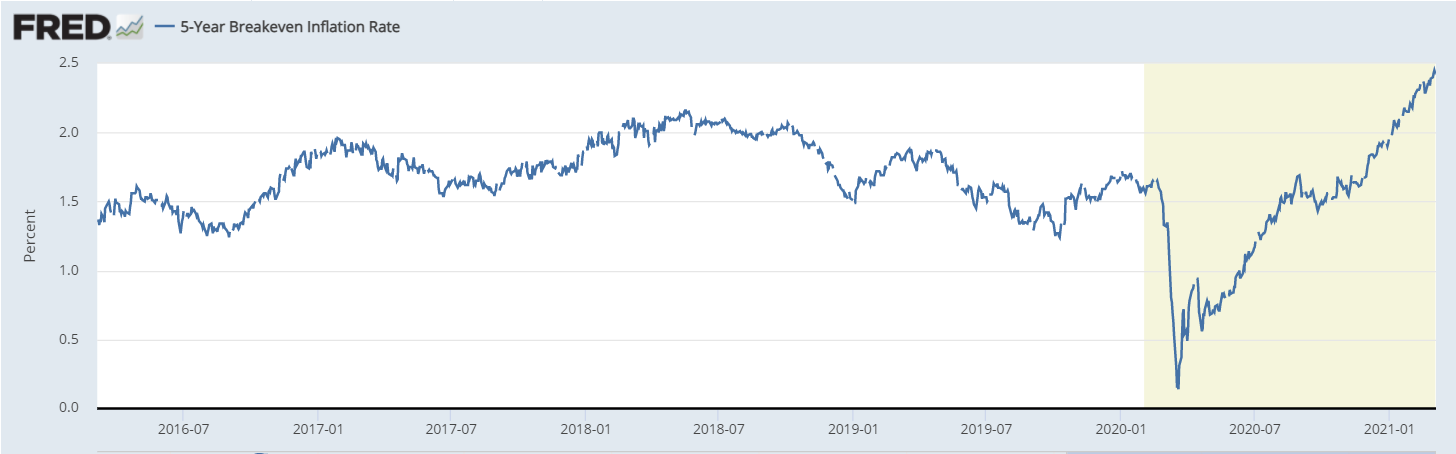
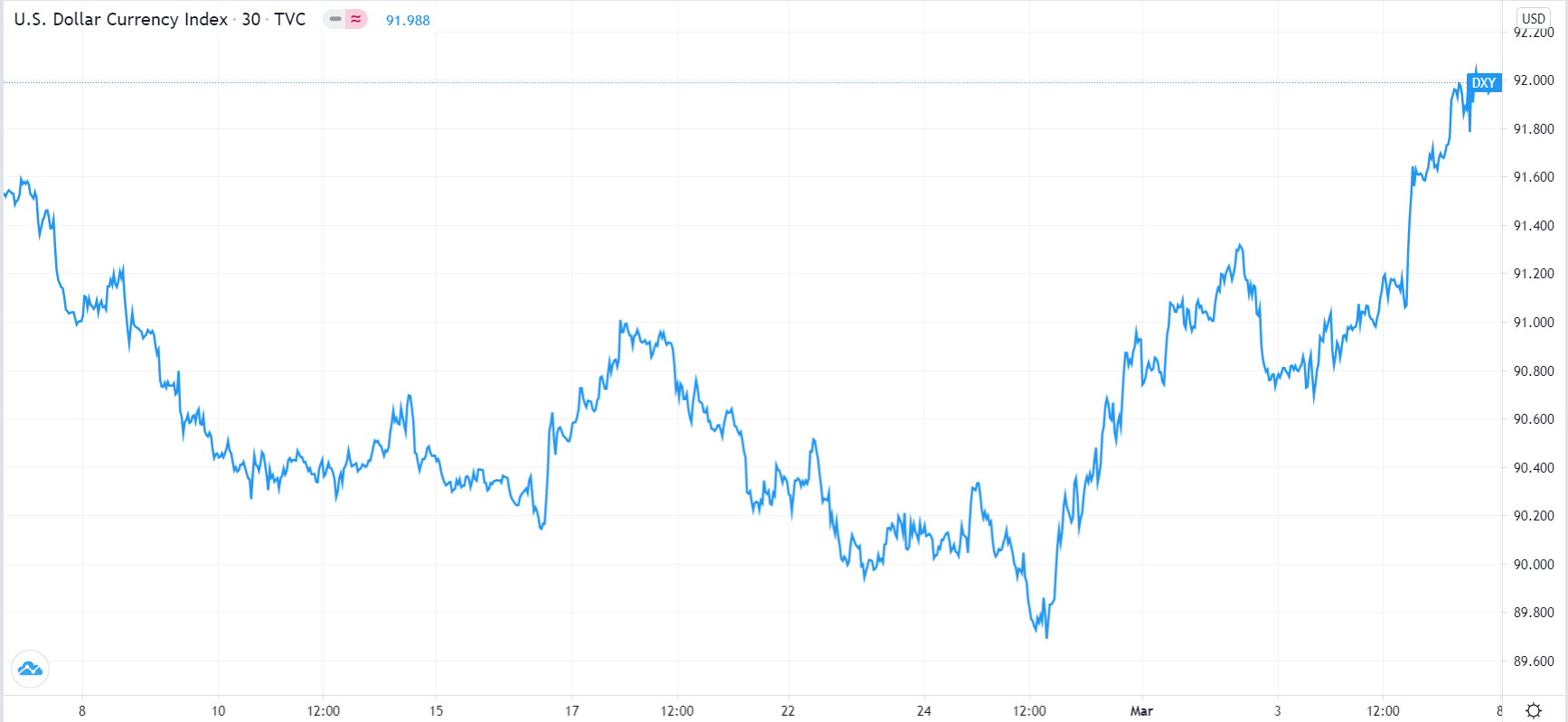
In early 2021, as the US yields rose, the US dollar index also rose, as shown below. This happened mostly because, as you can see above, the bond market was signaling that inflation would rise, leading to high-interest rates. As the dollar rises, risky assets like cryptocurrencies and emerging market currencies like the South African dollar, Mexican peso, and Turkish lira tend to weaken.
US dollar index chart
Another way of using the treasury yields in forex is to look at the inversion. Although it is rare, an inversion usually leads to safe assets like the US dollar and Swiss franc. Risky assets like emerging market currencies tend to weaken when it happens.
Final thoughts
In this article, we have looked at the role of the bond market, how it works, and the three types of bond yields. We have also identified how developed countries’ currencies like the US dollar and emerging market currencies usually react to the bond market.