GBPUSD perhaps is the only currency that has its own specific name – Cable. The name originated from the mid-19th century when a significant amount of communications used to happen via telegraph services. Messages between London and New York, the two major financial centres located across the Atlantic, took place through the physical cable that was laid through the ocean. So, whenever anyone was trading the GBPUSD pair, they would simply say they were trading ‘the cable.’
Fast forward to today, with the rise of electronic transactions, global currencies can be traded round the clock. GBPUSD is, in fact, the 3rd most traded currency, behind the EURUSD and USDJPY. Given the high amount of liquidity in the currency pair, traders find it easy to enter and exit positions.
Moreover, the pair represents two of the largest global economies that also have fairly transparent economic systems. As a result, news flow and key developments are continuously updated, offering many opportunities to profit from the pair’s volatility that results from the market’s reaction to the releases.
To understand the dynamics of GBPUSD, one needs to be aware of 3 major factors – the US economy and politics, the UK economy and politics, and the technical levels for the currency pair. Let us get into these in detail.
US economy and politics
There are two main drivers for the USD – the Federal Reserve, which is the monetary authority of the US, and the Federal Government. The Federal Reserve, through its fortnightly meetings, impacts the USD more frequently. It decides the money supply and the interest rates for the US dollar. The higher the money supply, the weaker the US dollar. Similarly, the lower the interest rates are, the weaker the US dollar. The present chairman of the Federal Reserve is Jerome Powell.
So, when the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets every six weeks, traders watch this event very closely. While the FOMC seldom changes rates or money supply. However, it does provide guidance for its future actions, which keeps on changing in nearly every meeting. There is significant volatility in GBPUSD around FOMC meetings. The calendar for these meetings is available on the Federal Reserve website, and every trader must keep track of these.
The Federal Government influences the GBPUSD through its fiscal policy. When the US government announces any major stimulus, it increases USD liquidity which weakens the dollar. These policies are highly influenced by the current party in power, the presidential election, and the midterm elections.
UK economy and politics
The UK economy is slightly different, as Britain initially was part of the European Union. Post-Brexit, the UK is no longer associated with the union. So, now its monetary policy is independent and governed by the Bank of England (BoE). The present governor of the Bank of England is Andrew Bailey. The BoE, too, meets every six weeks, and it publishes a comprehensive monetary policy report every quarter.
The central bank’s decisions on interest rates and monetary supply play a critical role in the strength of GBP. Unlike the US economy, the European economies have been undergoing a slowdown for the past couple of decades. This has led to the central banks being more supportive of growth and inclining towards lower rates for a prolonged period.
The UK government, too, plays a major role in deciding the strength of GBP. Although, over the past few years since the Brexit saga, it has witnessed multiple elections and changes in leadership. Following the Brexit referendum, David Cameron heading the conservative coalition, resigned.
Theresa May took over the position of Prime Minister in 2015, but within two years, she announced the snap elections. The elections led to a weaker mandate which was not expected, and, as a result, she too resigned soon afterward.
Finally, in the 2019 election, Boris Johnson won a clear majority for the conservative party and currently leads a government. It is worth noting that despite these multiple changes, the Conservative party has been in power since 2010, and there has been a political continuity in terms of policymaking.
The conservative party is known to show restraint on the fiscal front, which means they have not gone for massive spending programs. This has provided support to the GBP.
Pandemic and post-pandemic dynamics
Both the US and the UK have been among the leading countries in the world in terms of vaccinations. This means that they might see an early full-scale reopening of the economy ahead of the rest of the world.
However, the emergence of the Delta variant and resurgence in cases has created some concerns. On that front, there has been a spike in cases in the UK, prompting the government to delay certain reopenings. This has led to the UK economy somewhat lagging after the US economy. However, this might not continue for a long time.
A currency’s reserve status has also influenced the dynamics. GBP was the world’s primary reserve currency in the first half of the 20th century. However, by the end of the century, USD had become the reserve currency and continues to remain so. This reserve status gives the US the ability to create more debt since the rest of the world is ready to buy that debt, given USD’s safe status.
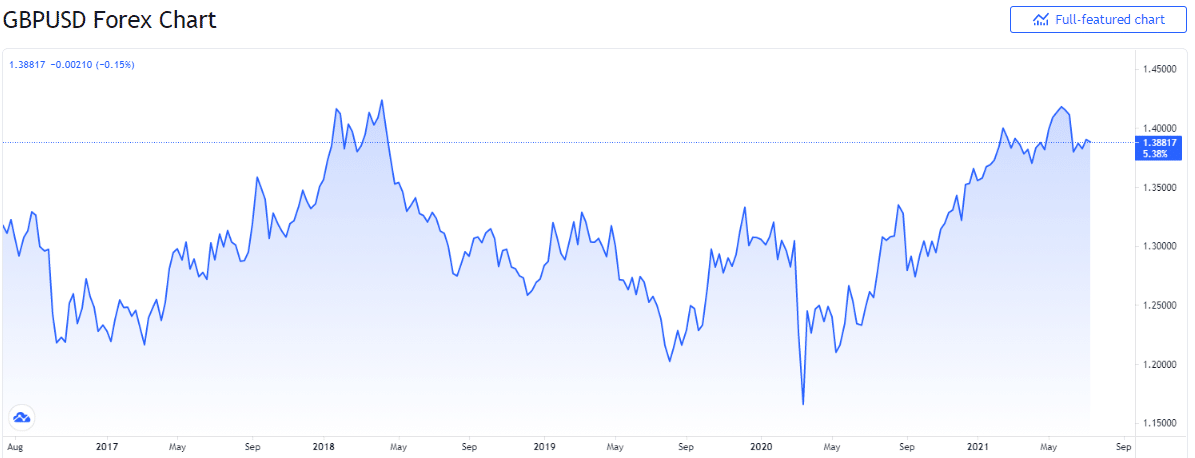
As seen above, the GBPUSD pair has traded in the range of 1.17 to 1.425. The lower end of the range was only because of the volatility driven by the Covid-19 pandemic. Otherwise, the critical support level has been in the 1.20 to 1.22.
Currently, it trades in the upper end of the range, with the price consistently rising since March 2020. One of the reasons for this move has been the massive easing undertaken by both the US government and the Federal Reserve. These measures are likely to taper soon. On the other hand, as can be seen in the chart, GBPUSD failed to go past the 1.42 level, indicating the price remains a strong resistance in the near term.